OOS In Pharma | OOS | Laboratory Investigation | Detailed Review
Out-of-specification (OOS) in the Pharma industry is one type of investigational tool used for laboratory investigations. Nowadays, the OOS is the first choice that is being inspected by regulatory inspectors during laboratory audits. More often OOS investigations are required in the pharmaceutical industry to identify the potential contributing factors that are affecting the quality of the product. So, in this post, we will cover the following,
1. What is OOS in pharma?
2. What are the basic concepts of the OOS?
3. How to investigate OOS?
What is the definition of out of specification mean (OOS)?
Those analytical test results which are falling outside the pre-determined approved specification limits are called out of specification results, for the same OOS handling procedure should be used.
During analysis, if the values are received out of set limit/specification/ standards that are called out of specification results.
|
OOS Case Study |
|||||
|
Case |
Product / Sample |
Test |
Limits |
Results |
Remark |
|
Case 1: |
ABC |
Assay of ABC |
95 to 105 % w/v |
94.89 % w/v |
OOS results |
|
Case 2 |
ABC |
Assay of ABC |
95 to 105 % w/v |
106.58 % w/v |
OOS results |
|
Case 3 |
ABC |
Assay of ABC |
95 to 105 % w/v |
103.58 % w/v |
Complying with the specification
limit |
|
Case 4 |
ABC |
Assay of ABC |
95 to 105 % w/v |
98.58 % w/v |
Complying with the specification
limit |
In simple language, those results which fall outside the pre-determined approved specification limits or acceptance criteria, are called OOS results.
What is an OOS investigation (Out of specification investigation)?
The OSS routinely happens at the laboratory. As per regulatory recommendation, there should be a confirmed cause behind the OOS. Unless and until the root cause of OOS is not identified we can not close the OOS. This is a current regulatory update that is being inspected during regulatory audits.
The OOS investigation is performed to identify the root cause of analytical failure and to have effective CAPA (Corrective Action and Preventive Action) for the failure. As we know, the analytical tests are being carried out in laboratories, and OOS are reported in the laboratory; however, there are chances that the cause of the OOS could be from product processing factors (Batch manufacturing process). As processing parameters directly impact quality parameters. Hence during the investigation, if the confirmed cause is not identified at the laboratory end, the investigation shall be extrapolated to batch processing activities. In this post, we have mentioned all the stages of OOS investigation.
What is Hypothesis testing in OOS investigation?
The OOS hypothesis is an idea that gives a possible explanation to find out the root cause of OOS. For e.g. Hypothesis means assuming that the cause is due to XYZ error and the XYZ error is repeated as a hypothesis plan. After repetition of assumed cause, if the test results are the same as OOS results, then the cause of the OOS is considered identified. The hypothesis is giving possibilities/predictions for the cause of the OOS which is unknown.
Pharmaceutical companies run according to regulatory requirements. There are rules and regulations for OOS handling procedures that are defined through regulatory requirements. Each pharmaceutical company should follow the procedure, otherwise, they will have lots of quality observations, 483's in audits.
Precautions to be taken during OOS investigation:
Confirmatory Testing in OOS Investigation:
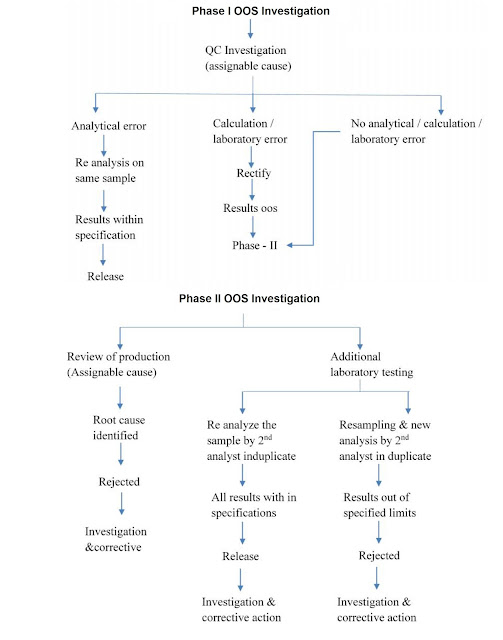
1. Phase I OOS Investigation- Initiation by reporting OOS and assessment of OOS results.
- First, we are going to report OOS and shall initiate the OOS handling procedure. The quality control coordinator reports it to the Quality Assurance coordinator after discussion with the head of the department.
- Quality Assurance personal alott specific OOS numbers for the identified OOS and issue OOS handling forms to the respective analysts.
- After this actual investigation starts, that is Phase I A.
- The obvious error may happen while doing analysis like calculation errors, equipment or Power failure, testing errors like incomplete transfer of sample or incorrect instrument parameters like incorrect runtime, wavelength, or incorrect method.
- If such an obvious error is identified means the investigation gets some positive conclusion. Then root cause for the discrepancy is said to be identified. CAPA (Corrective Action and Preventive Action) shall be implemented and then OOS can be closed.
- In Phase I A OOS investigation, if we didn't find any obvious error and the investigation comes to a negative conclusion then Phase I B starts. In this stage, the hypothesis plan shall be prepared by the investigation team.
- On some probable causes, the analysis shall be carried out as per the hypothesis plan. If we get some positive conclusion then CAPA shall be implemented and OOS shall be closed. Otherwise, the investigation moves further for phase II investigation.
- In phase I, if the cause is identified, then a confirmatory test is performed to confirm the root cause.
Most read posts:
2. Phase II OOS Investigation:
Phase II A OOS investigation:
It is a general review of production including investigation regarding batch-related parameters, Equipment parameters, environment parameters, Personnel, and other Production parameters.
In this general checks involved like equipment calibration, condition of equipment, preventive maintenance of equipment, where the equipment is inspected by QA or not? BMR for correct material and for correct total process, In-Process check results, Was personnel properly trained? Was the critical operation supervised by a supervisor? etc. This all should be considered but not limited.
Phase II B OOS investigation:
Phase II B OOS investigation includes additional laboratory testing by Re-sampling. In Phase, I all samples and additional samples was used for analysis by the first analyst and Senior Analyst or second analyst. At this stage, we need to re-sample the product to do a Re-analysis in duplicate By a second analyst. If all results are found within specification then the product shall be released and the investigation shall be closed with the CAPA plan.
If results fail, the material should be rejected. Phase III investigation shall be performed.
3. Phase III OOS investigation- Extended Investigation
This includes complete manufacturing, complete laboratory investigation Which includes Batch review, Method validation, Vendor evaluation, Impact on other batches, and then CAPA will implement for that. At this stage, if one can't get the root cause then it is difficult to explain to auditors.
This is an overall process that should be documented. At last whole case study shall be compiled with all analytical worksheets, all generated data, metadata and shall be reviewed. After that conclusion and closure of OOS are done.
Conclusion OOS:
For effective laboratory investigations, the OOS handling procedure is introduced in pharmaceutical as well as chemical laboratories. There are many challenges are observed during the OOS investigation. Hence to streamline and harmonize the laboratory investigation procedure; OOS needs to be implemented in pharma industries.
People also ask for,
|
OOS Guidelines to download: |
||
|
Sr. No. |
Guidance |
Click Download / View |
|
1 |
Investigating Out-of-Specification (OOS) Test Results
for Pharmaceutical Production - FDA Guidance on OOS |
|
|
2 |
Handling of OOS
Results in Europe - FDA Guidance on OOS |
|
|
3 |
Out of Specification Guidance - MHRA Inspectorate |
|
|
4 |
Handling of out of specification results -
Researchgate * |
|
👍👍
ReplyDeleteUclanitMen-hi Shane Sallah Free Download
ReplyDeletepretabtramin