Autoclave (Steam Sterilizer) | Detailed Review
Author: Mr. Rohit Ghadage E-mail: rohitghadage0109@gmail.com---------------------------------------------
Abstract:
The autoclave (Steam Sterilizer) is the "must" equipment of the sterile pharmaceutical company. The autoclave is the heart of sterile pharmaceutical companies. So, this post is for understanding the principles of autoclave operation, sterilization process, and qualification of the autoclave. As autoclave is a type of steam sterilization process, autoclave qualification is mandatory for all machinery used for biological sterilization in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industry within the FDA WHO, and EU regulations in accordance with cGMP. The elements of the autoclave qualification program of the biomedical and pharmaceutical industry should be clearly identified and documented
The purpose of this study is to initially develop the sterilization process parameter for the porous load articles then implement the sterilization process for the porous articles. The process development included the qualification of equipment and the articles. The autoclave cum bung processor is used for cleaning and sterilizing rubber stoppers, garments, and machine parts.
This was followed by performing the qualification of the equipment which describes the entire test right from the Steam quality test, Vacuum leak test, Bowie dick test, heat distribution test, and heat penetration test where equipment passes all tests and the equipment is suitable for sterilization purpose which is meeting its predetermined specification and quality attributes.
 |
| Autoclave (Steam Sterilizer) | Detailed Review |
1. Introduction to Autoclave (Steam Sterilizer):
Definition of Autoclave:
An autoclave is a pressure chamber used to carry out industrial processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure different from ambient air pressure. Autoclaves are used in medical applications to perform sterilization, and in the chemical industry to cure coatings, vulcanize rubber, and hydrothermal synthesis. (1)
Definition of Sterilization:
Sterilization can be defined as any process that effectively kills or eliminates microorganisms and transmissible agents (such as fungi, bacteria, viruses) from surfaces, equipment, foods, medications, and from the biological culture mediums. (2)
A sterility assurance level (SAL) of 10-6 means that there is less than or equal to one chance in millions that an item is contaminated or unsterile following the sterilization process. (3)
The autoclave was invented by Charles Chamber land in 1879. The name comes from Greek auto-self, and Latin clevis- key, a self-locking device. (4,5)
Autoclave Pressure, Sterilization Temperature, and Time:
|
Sr.
no. |
Temperature
(℃) |
Pressure(psi) |
Time |
|
1 |
115℃ |
10
psi |
30
minutes |
|
2 |
121℃ |
15
psi |
15
minutes |
|
3 |
132℃ |
27
psi |
10
minutes |
In university, autoclaves generally involve heating in saturated steam under a pressure of approximately 15 psi (10 bar) to achieve a chamber temperature of 121℃ (250 F). In fedegari autoclave to achieve chamber temperature of at least 121℃ to 124℃. In fedegari autoclave generally accepted that Sterility Assurance Level (SAL of 10-6)
Read more on steam sterilization:
1. Difference Between Sterilization and Depyrogenation
2. Steam sterilization validation in Autoclave:
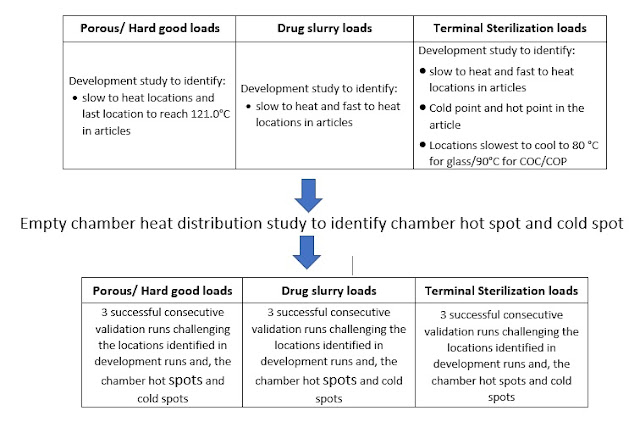
- Porous and Hard good loads:
- Drug slurry loads:
- Terminal sterilization of parenteral:
The initial validation of the Steam Sterilization process (porous I hard good, drug slurry loads, and terminal sterilization) shall be performed as per the tests in the approved Development and Validation Protocol. steam sterilization process validation can be summarized as below:
Types of Autoclave:
- Gravity displacement type autoclave: It is the most common type used in laboratories and is available in various sizes and dimensions.
- Vertical type (small volume capacity)
- Horizontal autoclave (large volume capacity)
- Positive pressure displacement type autoclave
- Negative pressure (vacuum) displacement type.
 |
| Types Of Autoclave |
Overview of steam sterilizer Validation (Autoclave validation):
3. Autoclave Qualification | Steam Sterilizer Qualification:
User requirement specification (URS) for Autoclave:
User or customer of equipment has a certain expectation about the equipment which wants to use. These expectations are generally in the form of his requirements. It is called user requirement specifications.
- To be issued by the User (Pharmaceutical Enterprise)
- Description of the sterilization process (e.g. standard sterilization, F0-sterilisation) on basis of the product properties s
- Definition of all (as possible) relevant GMP-critical points (e.g. sterility of cooling media, coldest spots)
- Definition of the user needs for documentation and operation (e.g. batch documentation, operating instructions etc.
- Completed by detailed technical specifications:
- The volume of the sterilization chamber
- Standards for electrical standards, wiring, valves,
- Standards for materials to be used (stainless steel) including surface roughness (< 0,8 µm or higher values?) \Interfaces to existing systems
- Drying / Air Filters (e.g. for stoppers for dry powder filling, cleanroom clothes)
- Definition of requirements for FAT / SAT
- A detailed description of requirements for Computer Validation
- Audit Trail
- User Access
- Backup / Recovery
- Disaster Recovery
- Definition of requirements for qualification (in case that supplier should support qualification)
Design qualification (DQ) for Autoclave:
Design qualification may verify that design of equipment, the system is as per the requirement of the user, and current good manufacturing practices.
→ Approval of DQ protocol and report respective approval of URS/FDS comparison by defined persons (VMP)
Factory Acceptance Test (FAT) / Site Acceptance Test (SAT) for Autoclave:
- Qualification staff should join FAT
- Preliminary documentation should be available and should be checked during FAT (incl. IQ and OQ - protocols)
- A first formal check of P&I-Diagram by qualification staff
- Definition of a test program on basis of supplier’s possibilities
- Structured FAT can substitute some IQ(OQ)-testing
- The basis for SAT should be mechanical completion of autoclave
- SAT should be performed as Pre-IQ / Pre-OQ / can substitute some IQ / OQ testing.
Installation qualification (IQ) for Autoclave:
Installation qualification is conducted to prove that equipment/system has been installed as per user and manufacturer recommendation and verify that all required utilities have provided safe operation of equipment/system.
- Utility specification
- Drawing specification (electrical, mechanical)
- Construction material in product contact ∙
- Operating and maintenance manual
Operational qualification (OQ) for Autoclave:
The operational qualification process is intended to demonstrate that the components are operating properly and ready for performance or load testing. Operational qualification shall be done “without load”.
Performance qualification (PQ) for Autoclave:
Performance qualification is documented evidence to prove that equipment/system is performing under specified conditions. It involves in taking a trial under “loaded condition”. 7
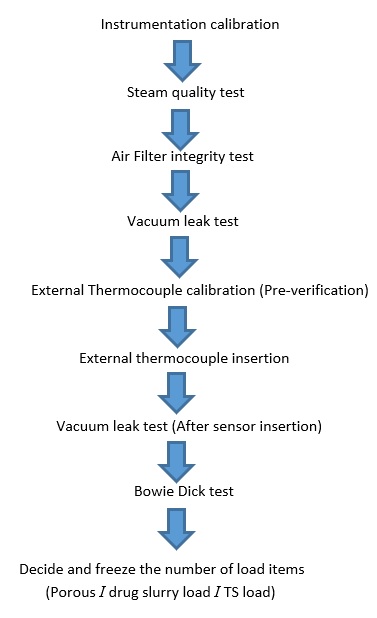
3. Qualitative Tests of Autoclave are:
I. Steam Quality Test for Autoclave:
Steam for sterilization requires a number of attributes in order to be an effective sterilant. Steam provides the moisture that allows the coagulation of cell wall proteins and supplies the energy that heats the components and maintains their temperature, the combination of temperature and moisture resulting in sterilization. The higher the temperature, the shorter the sterilization time required. Where steam comes into intimate contact with components that are either medical devices or that will come into contact with parenteral products, it should not add chemical or endotoxin contamination.
• Dryness Test
• Superheat Test:
Superheated steam is steam that is at an elevated temperature for its saturation pressure. It cannot be generated at the source by a conventional clean steam generator, as energy would have to be applied to the steam once it was in a dry saturated condition. Superheated steam is usually generated as the result of pressure drops through either pressure-reducing valves or orifices. The impact of the pressure drop is to modify the pressure of the steam while its energy content remains the same.
Superheat Test Acceptance criteria:
The test shall be considered satisfactory if the superheat measured in the expansion tube does not exceed 25°C.
• Non-Condensable Gases Test:
Non-condensable gases are gases liberated by steam when it condenses. The source of such gases is usually from the steam generator feedwater and the impact of such gases is that they modify the steam from being pure water vapor to a mixture of steam and gas and are therefore an unwanted contaminant. If we consider the heating of a single component by steam it will be seen that as steam condenses on the item its volume will reduce by a factor to 1/841 of the original value (for steam at 122o C).
This rapid reduction in volume causes a low-pressure area, which in turn is refilled with more steam. Until the product is heated, this process will continue. It will be seen that the flow of steam is always towards the component. As any gases are liberated at the point of condensation, it will be seen that any gases present in the steam will be forced by the flow of steam towards the product. If the component is hollow or porous, any liberated gases will be forced to the center. 8
Non-condensable Gases Test Acceptance criteria:
Read more on the steam quality test:
II. Vacuum Leak Test for Autoclave:
Objective:
Vacuum Leak Test Principle:
- The presence of air inhibits penetration of the load by the sterilant (Steam) and prevents sterilization.
- Air leaking into the chamber during the sterilization and drying cycle is not passed through the bacteria retentive filter, and therefore there is a risk of contamination of the load.
The test is performed by measuring the change in vacuum in the chamber when all the valves leading to it have been closed and the vacuum source is isolated.
The procedure of Vaccum leak test in Autoclave:
Ensure that the chamber temperature is stable at ambient and compressed air is on with high pressure and ensure that gasket lubrication is proper and switch provided on panel board. Start the vacuum leak rate test cycle and observe the pressure in the pressure gauge of the steam sterilizer and Cycle allows the pressure to the dropdown. The machine will close all the valves connected to the chamber and stop the vacuum pump and note the time and pressure (P1). Wait for a stabilization period of 5 minutes (±10 seconds) and note down the pressure again (P2) and Wait for another 10 minutes (± 10 seconds) and note down the pressure third time (P3). Return to atmospheric pressure and continue to run for the next cycle where vacuum leak rate should not be more than acceptance criteria.
Vacuum Leak Test Acceptance criteria:
Frequency:
III. Bowie- Dick test for Autoclave:
 |
Figure 1: Autoclave Bowie- Dick test Pack After Sterilization |
Procedure for bowie disk test of autoclave:
- Place the Bowie Dick test paper on the bottom shelf of the sterilizer just above the drain point (100mm over the drain).
- Air removal study shall be performed in the empty chamber by placing the Bowie Dick test paper. it consists of standard
- paper pack and indicator sheet Start the cycle by pressing enter key After the cycle is over open the door from the control area side and take the sterilized test paper from the autoclave and check the indicator paper for uniform color change As Bowie Dick test paper is designed to simulate the garment pack, it used to test the efficiency of the air removal from the steam sterilizer Three cycles of air removal study shall be performed (initially) by using fresh indicator paper This test shall be performed by using Bowie Dick test cycle. To fulfill the maximum exposure requirement, the sterilization cycle shall have 10 minutes at 121°C - 124°C sterilization period.
10 minutes’ cycle at a temperature of 121°C - 124°C. Place the Bowie dick indicator approximately 100 mm to 200 mm above the sterilization chamber base.
The Bowie dick indicator should show a uniform color change (Yellow to Brown/black) after the cycle. No change or no uniform change or air entrapment (bubbles) spot on the test sheet indicates inadequate air removal from the sterilization base chamber.
Run the test for 3 consecutive cycles at the time of Initial Qualification.
Objective:
To verify the temperature uniformity throughout the chamber and to locate the cold spot in the Empty Chamber. The sterilizer is capable of attaining a temperature of 121°C - 124°C throughout the sterilizing hold period in the Empty Chamber.
 |
| Figure 2: Heat distribution study In Autoclave (empty chamber) |
Procedure for heat distribution study in autoclave:
Insert 24 no of temperature sensors inside the chamber through the validation port of the sterilizer. Seal the port with silicone sealant to ensure that no steam leakage during operations of the sterilizer. Fix all the probes at different locations in the sterilizer so that sensors do not touch the metallic surface of the chamber. Connect the temperature sensors to the data logger, which can scan and print the actual temperature and pressure at different locations.
After completion of the sterilization cycle check the thermograph in the data logger for attaining set temperature and pressure during the sterilizing hold period. If any deviation is observed repeat the cycle after taking the necessary correction.
Temperature distribution within the chamber must be between 121°C - 124°C at all locations during the sterilization period (dwell time). There should not be any slowest heating point (cold spot) in the autoclave chamber and equilibrium time should not be more than 30 seconds.
V. Heat penetration study In Autoclave validation:
In order to verify sterilizing temperature has been reached in each load subjected to moist heat sterilization, it is necessary to conduct heat penetration studies. This study is conducted to ensure that the coolest unit within a predefined loading pattern (including minimum and maximum loads) will consistently be exposed to sufficient heat lethality (minimum "F0").
The procedure of Heat penetration study for Autoclave validation:
Insert 24 no of temperature sensors inside the chamber through the validation port of the sterilizer. Seal the port with silicone sealant to ensure that no steam leakage during operations of the sterilizer.
Fix all the probes at a different location in the sterilizer so that sensors do not touch the metallic surface of the chamber.
Load the article as per the loading pattern in the autoclave chamber. Loaded chamber heat distribution study shall be performed separately for all loading patterns. Arrange the load as specified keep at least 15 biological indicators and 10 thermochemical indicators shall be used for each cycle.
The load was placed at the identified cold points must-have indicator and temperature sensor in all three runs. One biological indicator and thermochemical indicator along with an external temperature sensor shall be placed at the drain point in all three cycles.
Perform the sterilization by operating the program specified for each load type as per standard operating procedure and start the data logger and steam sterilizer simultaneously.
After the sterilization cycle is completed, stop the data logger and open the sterilizer and take out the biological indicator and thermochemical indicator from the load and send them to the microbiology lab for testing.
The biological indicator shall aseptically inoculate into sterile soybean casein digest media (SCDM) and incubated at 55 - 60°C and liquid load at 35 - 39°C for 7 days and check the temperature.
Chemical indicator for the compliance as per manufacturer recommendation for color change (i.e. Brown). Take out temperature chart/data logger and inbuilt temperature recorder, report of the biological indicator. Check against acceptance criteria for compliance and determine the Fo value and compare against acceptance criteria. Take out an external temperature sensor from the chamber and perform a vacuum leak rate test.
Heat Penetration Study Acceptance Criteria:
Temperature distribution within the chamber must be between 121°C - 124°C at all locations during the sterilization period (dwell time). Sterilization temperature should be maintained for NLT 15 minutes for a minimum of 10 thermocouples during hold time. Biological indicator (Geobacillus Stearothermophillus) should show complete sterilization (i.e. no growth after incubation).
Uses of Autoclave
The autoclave is particularly useful for sterilization of porous as well as non-porous load. Generally, the things which are thermolabile can be autoclaved. However, the uses of autoclaves are tabulated below.
- Surgical instruments (Used for surgery)
- Pharmaceutical drug manufacturing accessories (For aseptic connection). Including scoops, vessels, forceps, SS mug, etc.
- Silicon tubes (Used for drug solution or WFI transfer)
- product filters, air filters (Used for product filtration)
- Drug slurry sterilization
- Garments (Used for cleanroom entries)
- Goggles (Used for cleanroom entries)
- Culture media
- Autoclavable plastic containers
- Plastic tubes and pipette tips
- Solutions and water
- Biohazardous waste
- For decontamination of media
- Glasswares
Conclusion on Autoclave operation, autoclave validation:
Qualification is a fundamental concept of cGMP. Where autoclave is used for sterilization of the garments, cleaning aids filters, utensils, vial filling machine parts, rubber stopper, etc.
This was followed by performing the qualification of the equipment which describes the entire test right from vacuum leak test, bowie-dick test, heat distribution study (empty chamber, loaded chamber), and heat penetration test.
All the parameters and processes mentioned need to be verified with predefined acceptance criteria before usage.

Great Blog. Provides valuable information. I visited it the very first time. And I appreciate your hard work. You can see my site if you want to find more on the biological indicator. While Biological Indicatorgives data on whether important conditions were met to kill a predetermined number of microorganisms.
ReplyDeleteThanks for writing such a great article on medical equipment, we are also one of the best India's manufacturers and suppliers of the below equipment. that is
ReplyDeleteDental UV chambers manufacturer in Delhi, Autoclave Cooker type manufacturer in Delhi, Dressing drum manufacturers in Delhi, Holloware manufacturers in Delhi, and Height scale manufacturers In Delhi
Informative article really, I was searching this type of blog to learn about it. To get more about https://www.haohongsealants.com/sealing-assembling-hardwares.html
ReplyDelete